Metamorphic Process Responsible For The Formation Of Marble
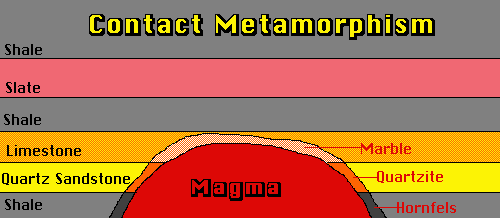
Limestone a sedimentary rock will change into the metamorphic rock marble if the right conditions are met.
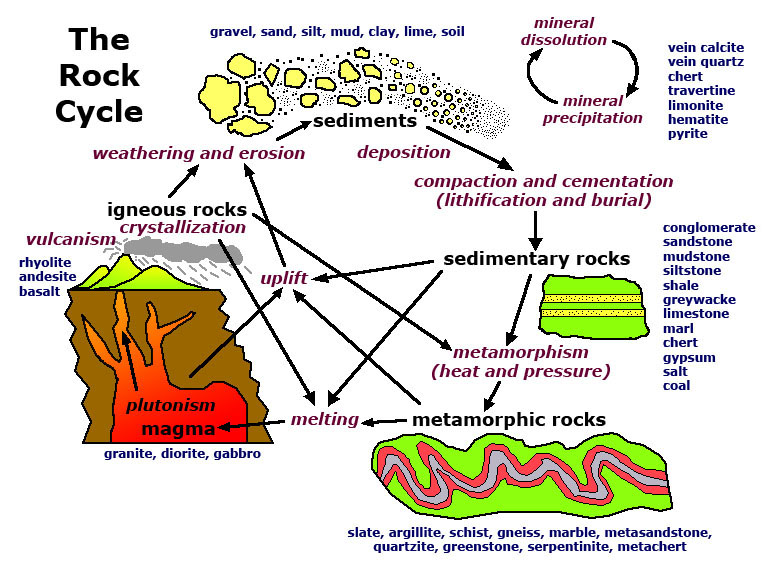
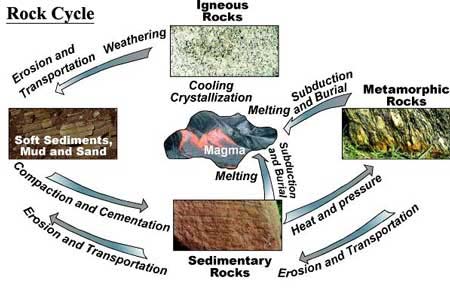
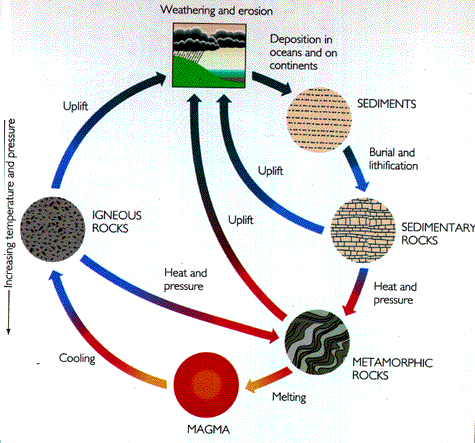
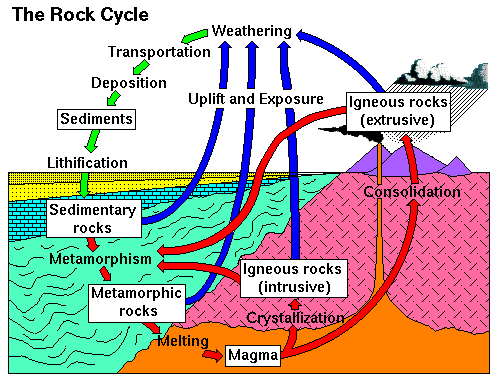
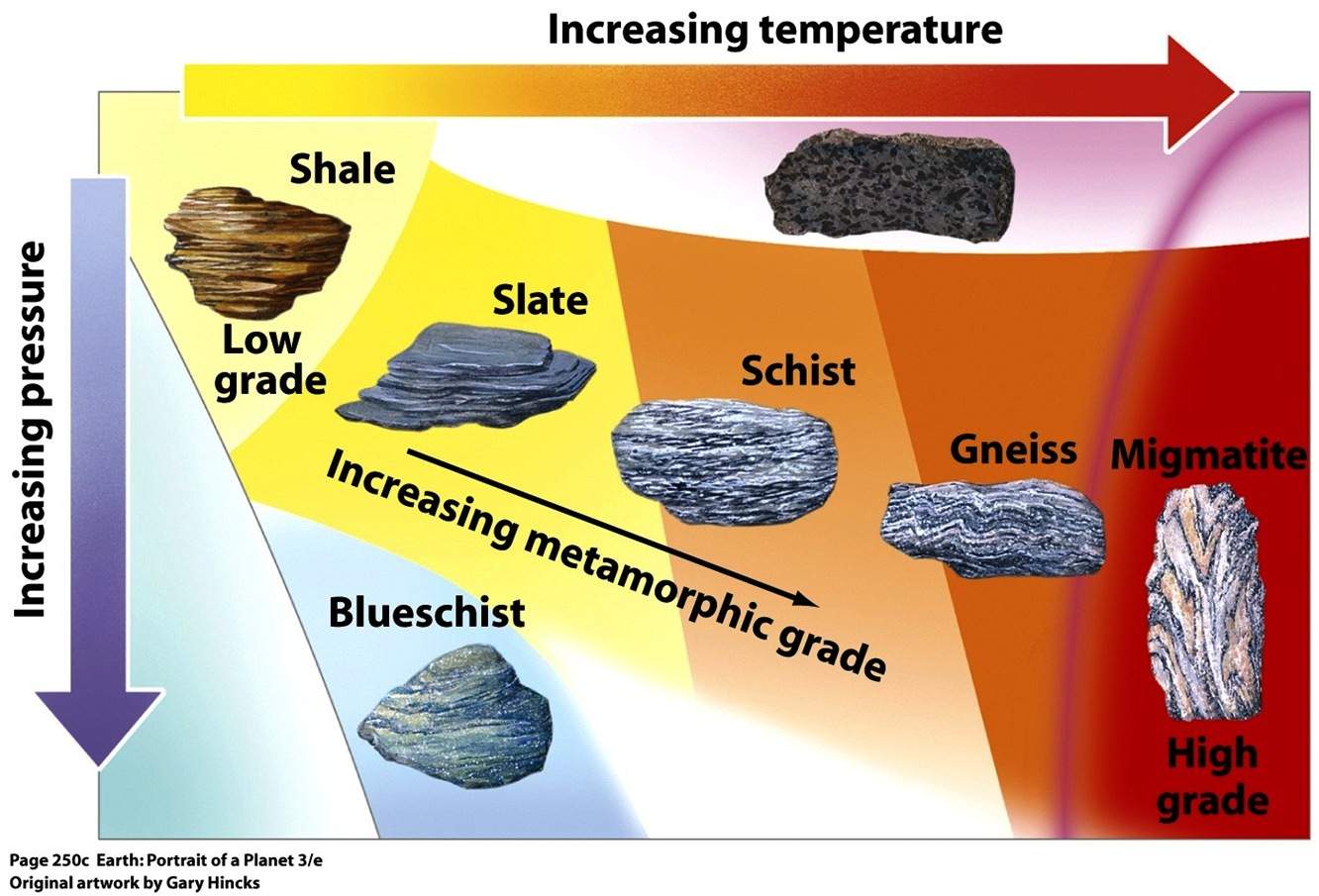
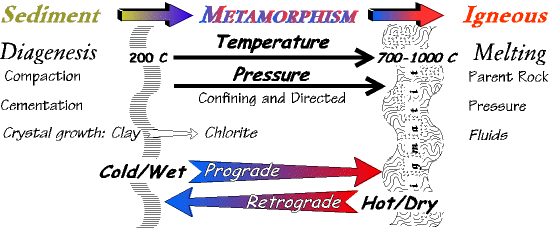
Metamorphic process responsible for the formation of marble. The pressures and temperatures essential to produce this stone generally eliminate any fossils that exist in the initial rock. Neometamorphism or neocrystallization is a metamorphic process that results in the formation of new minerals. Marble is a metamorphic rock produced from limestone by pressure and heat in the earth crust due to geological processes. Metamorphic rock any rock that results from the alteration of preexisting rocks in response to changing conditions such as variations in temperature pressure and mechanical stress and the addition or subtraction of chemical components.
The preexisting rocks may be igneous sedimentary or other metamorphic rocks. Slate is another common metamorphic rock that forms from shale. As per wikipedia metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock types in a process called metamorphism which means change in form the original rock protolith is subjected to heat temperatures greater than 150 to 200 c and pressure 1500 bars causing profound physical and or chemical change. This is seen when limestone recrystallizes into marble.
Marble is commonly used for sculpture and as a building material. When the heat and pressure hits the limestone calcite seed crystals form. Because marble is a fairly soft material only a three on the mohs hardness scale it is easy to cut and carve. Due to these forces the texture of limestone is changed.
It is composed primarily of the mineral calcite caco 3 and usually contains other minerals such as clay minerals micas quartz pyrite iron oxides and graphite under the conditions of metamorphism the calcite in the limestone recrystallizes to form a rock that is. Marble is a metamorphic rock that forms when limestone is subjected to the heat and pressure of metamorphism. Although metamorphic rocks typically form deep in the planet s crust they are often exposed on the surface of the earth.