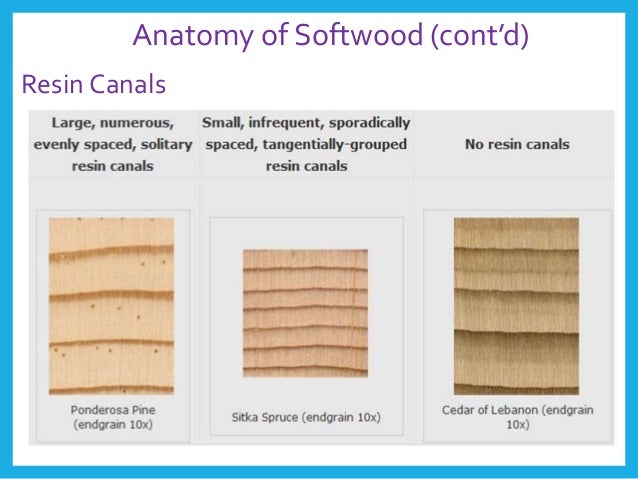
Microscopic Example Of Softwood And Hardwood
An unknown hardwood sample could be just about anything under the sun yet as each anatomical feature is considered anything is narrowed down to something.
Microscopic example of softwood and hardwood. In simple terms timber from coniferous tree is the softwood and timber from a deciduous tree is the hardwood. Examples of softwood trees are cedar douglas fir juniper pine redwood spruce and yew. Most softwoods have a lower density than most hardwoods. Please read more on density here.
Softwoods are made of tracheids and parenchyma and hardwoods of vessel members fibres. Nonetheless even though hardwood parenchyma cells can form much more complex and telling arrangements softwood parenchyma still have a limited use in identification. Likewise balsa wood is classified as a hardwood and yet it s one of the least dense and softest types of wood. According to estimates 1 cubic metre about 35 cubic feet of spruce wood contains 350 billion 500 billion cells.
From angiosperm trees that are not monocots and usually broad leaved and has vessel elements that transport water throughout the wood hardwood is formed and these elements appear as pores under a microscope. That is hardwood isn t necessarily denser than softwood. Examples of hardwood trees include. The basic cell types are called tracheids vessel members fibres and parenchyma.
Most hardwoods have a higher density than most softwoods. Alder balsa beech hickory mahogany maple oak teak walnut softwood comes from gymnosperm. For example balsa wood is known as one of the softest and least dense types of wood yet it is categorized as hardwood. That is to say throughout the identification process the more observations that can be made and classified about a hardwood sample the more and more the field of possible candidates narrows.
Hardwood comes from angiosperm trees that are not monocots. Parenchyma cells are an example of an anatomical element that is of much greater use in macroscopic hardwood identification than it is in softwood identification. Most do not shed their needle like leaves during the year. Under a microscope these woods do not seem to have any visible pores because of the presence of the tracheids.
Wood wood microstructure. In softwoods the tracheids and medullar rays are responsible for producing sap and transporting water within the wood. Most softwood have a lower density than hardwood weighs lower. Similarly wood from the yew tree which is one of the toughest woods and is harder than most types of oak is classified as softwood.
The softwood larch and cypress are exceptions. For instance yew wood is classified as a softwood but is considerably tougher than certain hardwoods. Wood is categorized as either softwood or hardwood based on physical structure and makeup. The microscope reveals that wood is composed of minute units called cells.
They have vessel elements that transport water throughout the wood under a microscope these elements appear as pores. Hardwood is typically more expensive than softwood. Softwood is typically less expensive compared to hardwood.

















